Gift of Equity: The Complete Guide to Family-Assisted Home Purchases
Gift of equity represents one of the most powerful yet underutilized strategies for first-time homebuyers entering today’s challenging real estate market. This financial tool allows family members to transfer property wealth while providing significant advantages for both buyers and sellers. According to the National Association of Realtors, approximately 15% of first-time buyers receive some form of family assistance, yet many families miss the opportunity to structure these transactions optimally through gift of equity provisions.

[Image: Visual diagram showing gift of equity transaction flow between family members, lender, and closing process]
Table of Contents
- Understanding Gift of Equity Fundamentals
- Qualifying Relationships and Legal Requirements
- Step-by-Step Implementation Process
- Financial Benefits and Tax Implications
- Lender Requirements and Documentation
- State-Specific Regulations and Variations
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Builds and Buys Framework: Gift of Equity Strategy
Understanding Gift of Equity Fundamentals
Gift of equity occurs when a property owner sells their home to a family member for less than market value, with the difference serving as the buyer’s down payment. Unlike traditional down payment gifts that require actual cash transfers, gift of equity creates equity instantly through the transaction structure itself.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau recognizes gift of equity as a legitimate source of funds for home purchases, providing specific guidelines for implementation. This mechanism transforms family property transfers into powerful wealth-building opportunities while maintaining compliance with lending regulations.
Key Components of Gift of Equity
Market value determination forms the foundation of any gift of equity transaction. Professional appraisals establish fair market value, creating the baseline from which the gift amount gets calculated. The Federal Housing Administration requires arms-length appraisals even for family transactions, ensuring legitimate valuations.
Purchase price agreement reflects the actual amount the buyer pays, which must be below appraised value to create the equity gift. The difference between appraised value and purchase price constitutes the gift amount, directly reducing or eliminating the buyer’s down payment requirement.
Down payment credit applies the gift amount toward the buyer’s required down payment and potentially closing costs. Most conventional loans require 20% down to avoid private mortgage insurance, making gift of equity particularly valuable for buyers lacking substantial savings.
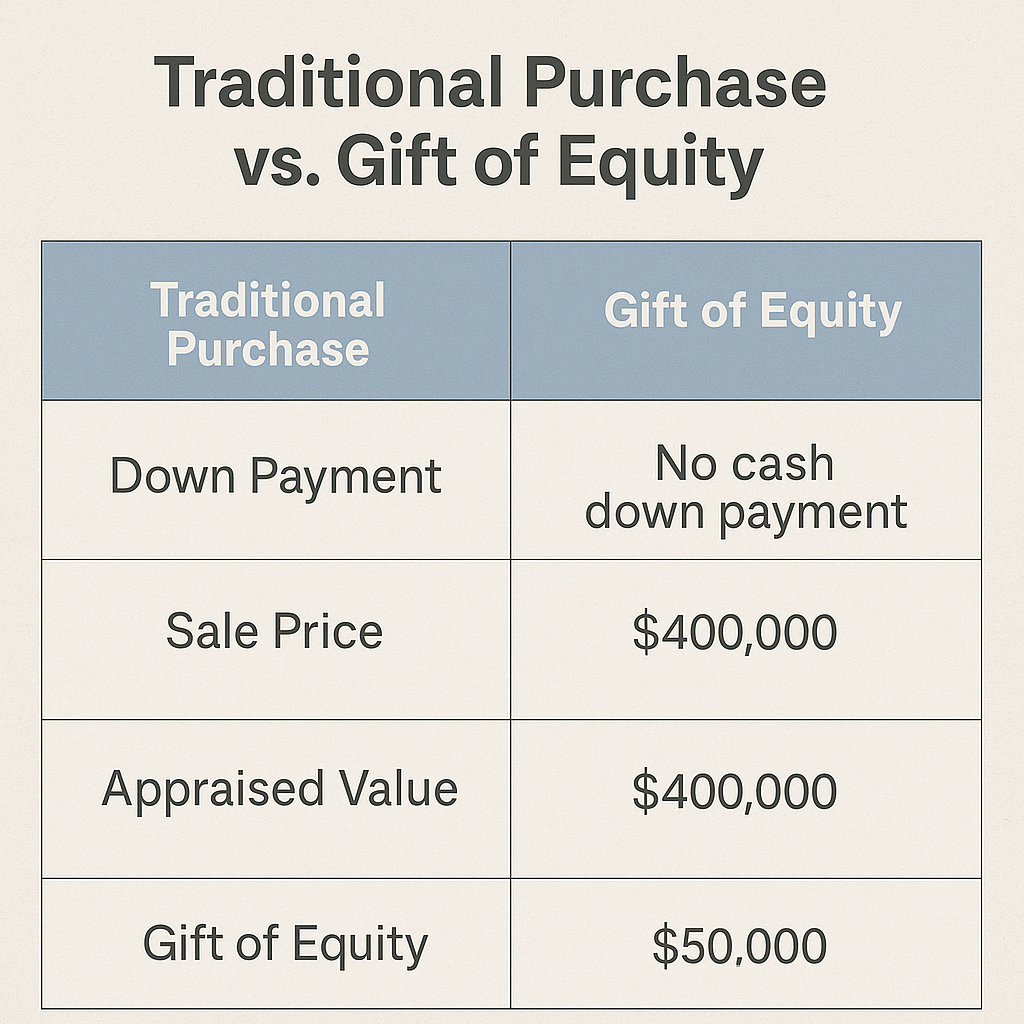
[Image: Comparison chart showing traditional purchase with cash down payment versus gift of equity structure]
Real-World Example
Consider a property appraised at $400,000 where parents sell to their adult child for $320,000:
| Transaction Component | Amount | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Appraised Market Value | $400,000 | 100% |
| Agreed Purchase Price | $320,000 | 80% |
| Gift of Equity Amount | $80,000 | 20% |
| Buyer’s Cash Needed at Closing | $0 | 0% |
| Loan Amount (if no additional down payment) | $320,000 | 80% LTV |
This structure eliminates private mortgage insurance requirements while providing the buyer immediate equity, demonstrating the power of properly structured family transfers.
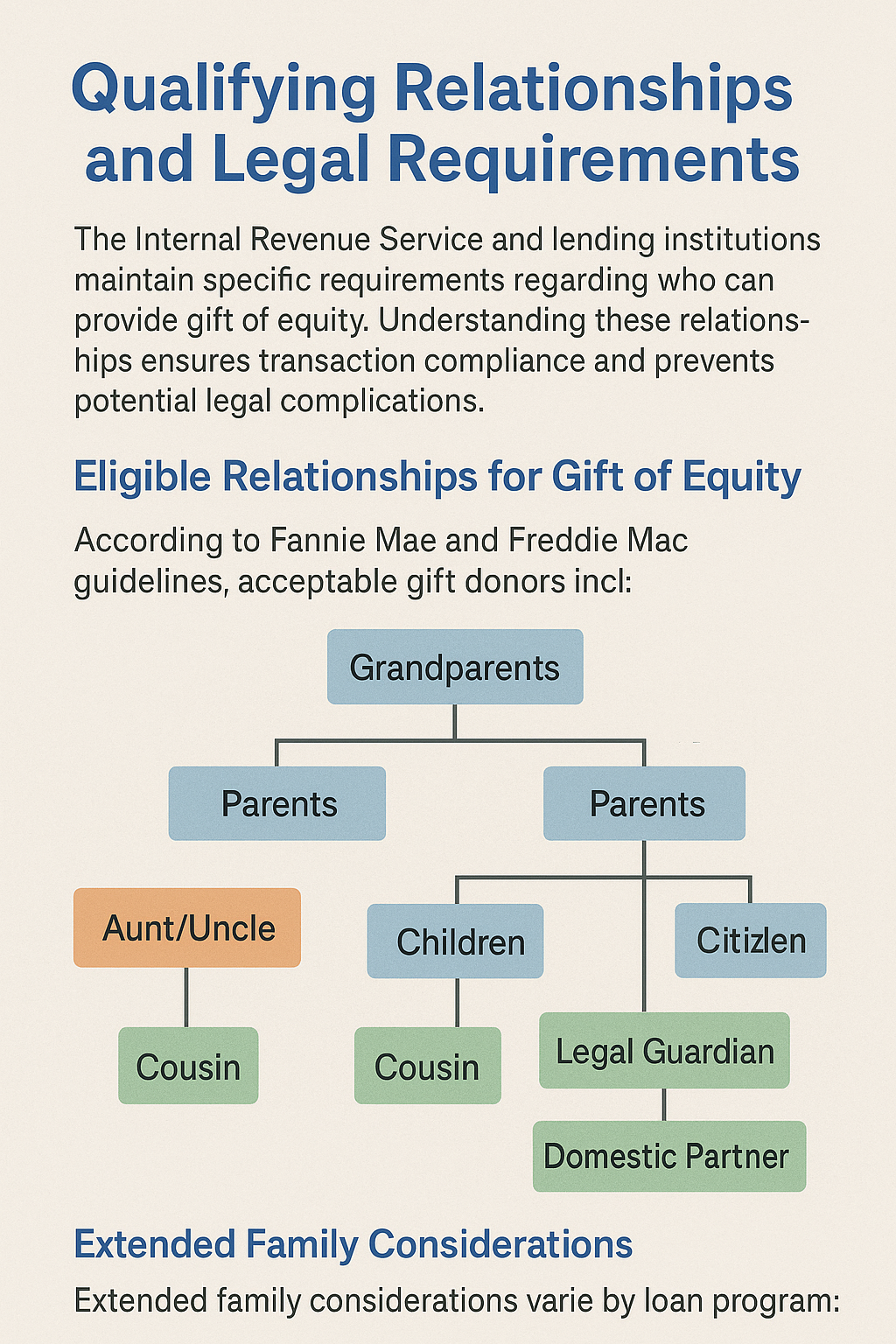
Qualifying Relationships and Legal Requirements
The Internal Revenue Service and lending institutions maintain specific requirements regarding who can provide gift of equity. Understanding these relationships ensures transaction compliance and prevents potential legal complications.
Eligible Relationships for Gift of Equity
According to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac guidelines, acceptable gift donors include:
Immediate Family Members
Immediate family members represent the most common and straightforward gift of equity providers:
- Parents to children (including stepparents and adoptive parents)
- Grandparents to grandchildren
- Siblings to siblings (including half-siblings)
- Children to parents (less common but allowable)
- Spouses to each other (in specific circumstances)
Extended Family Considerations
Extended family considerations vary by loan program:
- Aunts and uncles (accepted by FHA, varies for conventional)
- Cousins (generally only with FHA loans)
- Legal guardians (with proper documentation)
- Domestic partners (depending on state laws and lender policies)
[Image: Family tree diagram showing eligible gift of equity relationships with color coding for different loan programs]
Legal Documentation Requirements
Proper documentation protects all parties and satisfies lender requirements. The National Association of Realtors emphasizes that family transactions require the same legal rigor as arms-length sales.
Purchase Agreement Specifications
Must clearly state:
- Relationship between buyer and seller
- Agreed purchase price below market value
- Explicit mention of gift of equity amount
- Statement that gift requires no repayment
- Signatures from all parties involved
Gift Letter Requirements
Include specific mandatory elements:
- Donor’s name, address, and relationship to recipient
- Property address and purchase price
- Explicit gift amount and statement of no repayment
- Donor’s affirmation of financial ability to provide gift
- Statement that funds aren’t borrowed
- Dated signatures from all donors
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Successfully executing a gift of equity transaction requires careful coordination between family members, lenders, and closing professionals. Following this systematic approach ensures smooth transaction completion while maximizing financial benefits.
Step 1: Establish Property Value
Order a professional appraisal from a licensed appraiser to establish current market value. This appraisal must be ordered through the lender to meet underwriting requirements. The appraiser should be informed this is a family transaction but must still provide an unbiased market valuation.
Cost: $400-$800 depending on property type and location
Timeline: 5-10 business days from order to report
Step 2: Determine Gift Amount
Calculate the gift of equity by subtracting the agreed purchase price from the appraised value. Consider the buyer’s loan program requirements and whether additional cash will be needed for closing costs. Most conventional loans allow gift of equity to cover the entire down payment.
Tip: Structure the gift to achieve at least 20% equity to avoid PMI
Consider: Closing costs typically run 2-5% of purchase price
Step 3: Select Appropriate Financing
Work with a mortgage professional experienced in gift of equity transactions. Different loan programs have varying requirements for gift amounts and documentation. FHA loans are often more flexible with gift sources, while conventional loans may offer better rates with sufficient equity.
Options: Conventional, FHA, VA (if eligible), USDA (rural properties)
Key Factor: Ensure lender is familiar with gift of equity procedures
Step 4: Prepare Documentation
Compile all required documentation including the gift letter, purchase agreement with gift of equity addendum, and any additional lender-required forms. Ensure all parties understand the transaction structure and have reviewed documents with appropriate advisors.
Essential Documents: Gift letter, purchase agreement, proof of relationship
Timeline: Complete all documentation before loan application
Step 5: Close the Transaction
Proceed through standard closing procedures with special attention to gift documentation. The settlement statement will reflect the gift of equity as a credit to the buyer. Sellers receive their net proceeds based on the agreed purchase price, while buyers gain immediate equity.
At Closing: Review HUD-1 or Closing Disclosure for accuracy
Verify: Gift amount properly credited on settlement statement
Financial Benefits and Tax Implications
Gift of equity transactions provide substantial financial advantages for both buyers and sellers when properly structured. Understanding these benefits and associated tax implications ensures optimal transaction outcomes while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations.
Buyer Financial Benefits
Immediate Equity Position
Buyers gain instant equity equal to the gift amount, providing financial cushion and potential borrowing power for future improvements or emergencies.
PMI Avoidance
Reaching 20% equity through gift eliminates private mortgage insurance, saving $100-300 monthly on typical loan amounts.
No Cash Required
Eliminates the need to save for years to accumulate down payment funds, enabling immediate homeownership.
Better Loan Terms
Higher equity positions often qualify for better interest rates, potentially saving thousands over the loan term.
Tax Implications and Considerations
The Internal Revenue Service treats gift of equity as a non-cash gift subject to gift tax regulations. Both parties should understand these implications before proceeding with the transaction.
| Tax Consideration | 2024 Limits | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Gift Tax Exclusion | $18,000 per person | Gifts below this amount require no tax filing |
| Lifetime Gift Tax Exemption | $13.61 million | Larger gifts reduce lifetime exemption |
| Married Couple Combined Annual Exclusion | $36,000 per recipient | Doubles exclusion for joint gifts |
| Capital Gains Basis | Transferred to buyer | Buyer inherits seller’s tax basis |
⚠️ Important Tax Consideration
Consult with a qualified tax professional before proceeding with any gift of equity transaction. Tax implications vary based on individual circumstances, gift amounts, and state regulations. Proper planning can minimize tax obligations while maximizing transaction benefits.
Lender Requirements and Documentation
Different loan programs maintain specific requirements for gift of equity transactions. Understanding these requirements ensures smooth loan approval and prevents last-minute complications that could delay or derail closing.
Loan Program Requirements
Conventional Loans (Fannie Mae/Freddie Mac)
- Gift from immediate family members acceptable
- Can cover entire down payment and closing costs
- No minimum buyer contribution required
- Gift letter must meet specific format requirements
- Property must be primary residence or second home
FHA Loans
- More flexible on acceptable donor relationships
- Can cover entire down payment (3.5% minimum)
- Allows gifts from extended family members
- Requires evidence of donor’s ability to gift
- Subject to FHA property standards and limits
VA Loans
- Gift of equity allowed from immediate family
- No down payment required, but gift can cover closing costs
- Must meet VA occupancy requirements
- Property must pass VA appraisal standards
- Veteran must still pay VA funding fee unless exempt
Required Documentation Checklist
Primary Documents
- Completed gift letter with all required elements
- Purchase agreement noting gift of equity
- Professional appraisal report
- Proof of relationship documentation
- Seller’s proof of ownership
Supporting Documents
- Donor’s bank statements (if required)
- Buyer’s employment verification
- Buyer’s asset documentation
- Title/deed showing seller ownership
- Any additional lender requirements
State-Specific Regulations and Variations
While gift of equity transactions are recognized nationwide, individual states maintain specific regulations affecting implementation. Understanding your state’s requirements ensures compliance and prevents unexpected complications.
Key State Variations
| State/Region | Special Considerations | Documentation Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| California | Transfer tax calculations based on full value | Preliminary Change of Ownership Report required |
| Texas | No state income tax benefits | Gift affidavit may be required by county |
| New York | Mansion tax may apply on high-value properties | TP-584 transfer tax form required |
| Florida | Documentary stamp tax on full value | Specific gift disclosure requirements |
| Illinois | Real estate transfer tax considerations | PTAX-203 Illinois Real Estate Transfer Declaration |
Transfer Tax Implications
Many states calculate transfer taxes based on full market value rather than purchase price. Budget for these costs based on appraised value, not the reduced purchase amount.
Recording Requirements
Some jurisdictions require specific language in deeds noting the family relationship and gift component. Verify local recording requirements early in the process.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning from common errors helps ensure smooth transaction completion. These mistakes can delay closing, increase costs, or even cause transaction failure.
Mistake #1: Incorrect Documentation
Problem: Generic gift letters or missing required elements cause underwriting delays and potential loan denial.
Solution: Use lender-provided templates and include all required elements. Have documents reviewed before submission.
Prevention Tip: Request gift letter template from lender at application, not days before closing.
Mistake #2: Improper Valuation
Problem: Using outdated appraisals or informal valuations creates compliance issues and loan problems.
Solution: Order fresh appraisal through the lender following standard procedures. Never rely on tax assessments or online estimates.
Prevention Tip: Appraisals typically valid for 120 days; plan transaction timeline accordingly.
Mistake #3: Tax Planning Oversights
Problem: Failing to consider gift tax implications or capital gains basis transfer creates unexpected tax liabilities.
Solution: Consult tax professionals before finalizing transaction structure. Consider spreading gifts across tax years if needed.
Prevention Tip: File Form 709 if gift exceeds annual exclusion to preserve lifetime exemption.
Mistake #4: Inadequate Buyer Qualification
Problem: Assuming gift of equity guarantees loan approval leads to failed transactions when buyers don’t qualify.
Solution: Complete full loan pre-approval before proceeding. Gift of equity helps with down payment but doesn’t improve credit or income qualification.
Prevention Tip: Obtain written pre-approval letter specifically mentioning gift of equity structure.
Builds and Buys Framework: Gift of Equity Strategy
At Builds and Buys, we’ve developed comprehensive strategies for maximizing gift of equity benefits across our three core pillars: building, buying, and investing in real estate.
Step-by-Step Builds
Leverage gift of equity when family members own buildable land. Structure transfers to maintain equity while enabling new construction financing.
Explore Building Strategies →Step-by-Step Buys
Navigate the complete purchase process with gift of equity, from initial family discussions through successful closing.
Explore Buying Process →Step-by-Step Invest
Transform family property transfers into investment opportunities through strategic planning and proper structuring.
Explore Investment Options →Strategic Implementation Guidelines
For First-Time Buyers
Gift of equity eliminates the primary barrier to homeownership – the down payment. Structure transactions to maximize immediate equity while ensuring sustainable monthly payments. Consider combining gift of equity with first-time buyer programs for additional benefits.
For Real Estate Investors
Use gift of equity to acquire family properties with built-in equity for renovation or rental conversion. Structure transactions to preserve capital for improvements while maintaining family wealth within the extended family network.
For Multi-Generational Planning
Implement gift of equity as part of comprehensive estate planning. Transfer property wealth while parents are living, potentially reducing estate taxes and ensuring smooth property transitions to the next generation.
Take Action: Implement Your Gift of Equity Strategy
Gift of equity transforms family property transfers into powerful wealth-building opportunities. Whether you’re a first-time buyer seeking homeownership or a family planning multi-generational wealth transfer, proper implementation ensures maximum benefits while maintaining compliance.
Ready to explore your options?
Connect with mortgage professionals experienced in gift of equity transactions to begin your journey.
Sample Gift of Equity Letter Template
[Date]
[Lender Name and Address]
RE: Gift of Equity for [Buyer’s Full Name]
Property Address: [Full Property Address]
To Whom It May Concern:
I/We, [Donor’s Full Name(s)], am/are providing a gift of equity to [Recipient’s Full Name], my/our [Relationship], in the amount of $[Gift Amount] for the purchase of the above-referenced property.
This gift represents the difference between the appraised value of $[Appraised Value] and the purchase price of $[Purchase Price].
I/We certify that:
• This is a bona fide gift with no repayment expected or implied
• The funds for this gift are my/our own and not borrowed
• I/We have no financial interest in the transaction beyond the sale
• This gift is being made solely to assist the buyer with the purchase
Sincerely,
_________________________ Date: _______
[Donor’s Signature]
[Donor’s Printed Name]
Related Resources
Expand your real estate knowledge with these comprehensive guides:
First-Time Buyer Guide
Complete roadmap for navigating your first home purchase with confidence.
Learn More →Investment Property Basics
Transform real estate into wealth through strategic investment planning.
Learn More →Building Your Dream Home
Step-by-step guidance for successful new construction projects.
Learn More →




