
Check out our app!
Explore more features on mobile.
What is Real Estate? A Comprehensive Guide to Property, Investment, and Wealth Building
Published on 2025/04/04
Real estate is more than just land and buildings—it’s a dynamic asset class that drives economies, creates wealth, and shapes communities. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer, an aspiring investor, or a developer, understanding real estate’s fundamentals is critical. This guide breaks down the types of real estate, market trends, financial strategies, and step-by-step frameworks to help you navigate this complex industry with confidence.

Real estate spans residential, commercial, industrial, and land assets.
1. The Definition of Real Estate
Real estate refers to land and any permanent structures attached to it, whether natural (trees, water) or man-made (homes, offices). It’s categorized by its use and includes rights to air, mineral, and underground resources. Unlike personal property (cars, furniture), real estate is immovable and governed by location-specific laws.
Key Characteristics:
- Scarcity: Land supply is finite, driving value in high-demand areas.
- Location Dependency: A property’s value hinges on neighborhood, amenities, and economic activity.
- Durability: Real estate is a long-term asset with depreciation timelines spanning decades.
2. The 4 Main Types of Real Estate
A. Residential Real Estate
Properties designed for living, including:
- Single-family homes
- Multi-family units (duplexes, apartments)
- Condominiums and townhouses
- Vacation homes
Market Insight: U.S. median home prices rose to $412,000 in 2024 (National Association of Realtors), with rental demand surging in suburban areas post-pandemic.
B. Commercial Real Estate
Income-generating properties like:
- Office buildings
- Retail spaces (malls, stores)
- Hotels and hospitality venues
Trend Alert: Hybrid work models have reshaped office space demand, with a 15% vacancy rate in major cities (CBRE, 2024). Adaptive reuse (converting offices to apartments) is gaining traction.
C. Industrial Real Estate
Facilities for manufacturing, storage, and logistics:
- Warehouses
- Factories
- Distribution centers
Data Point: E-commerce growth fueled a 34% spike in warehouse leasing since 2020 (JLL Research).
D. Land
Undeveloped plots used for:
- Agriculture
- Future development
- Conservation
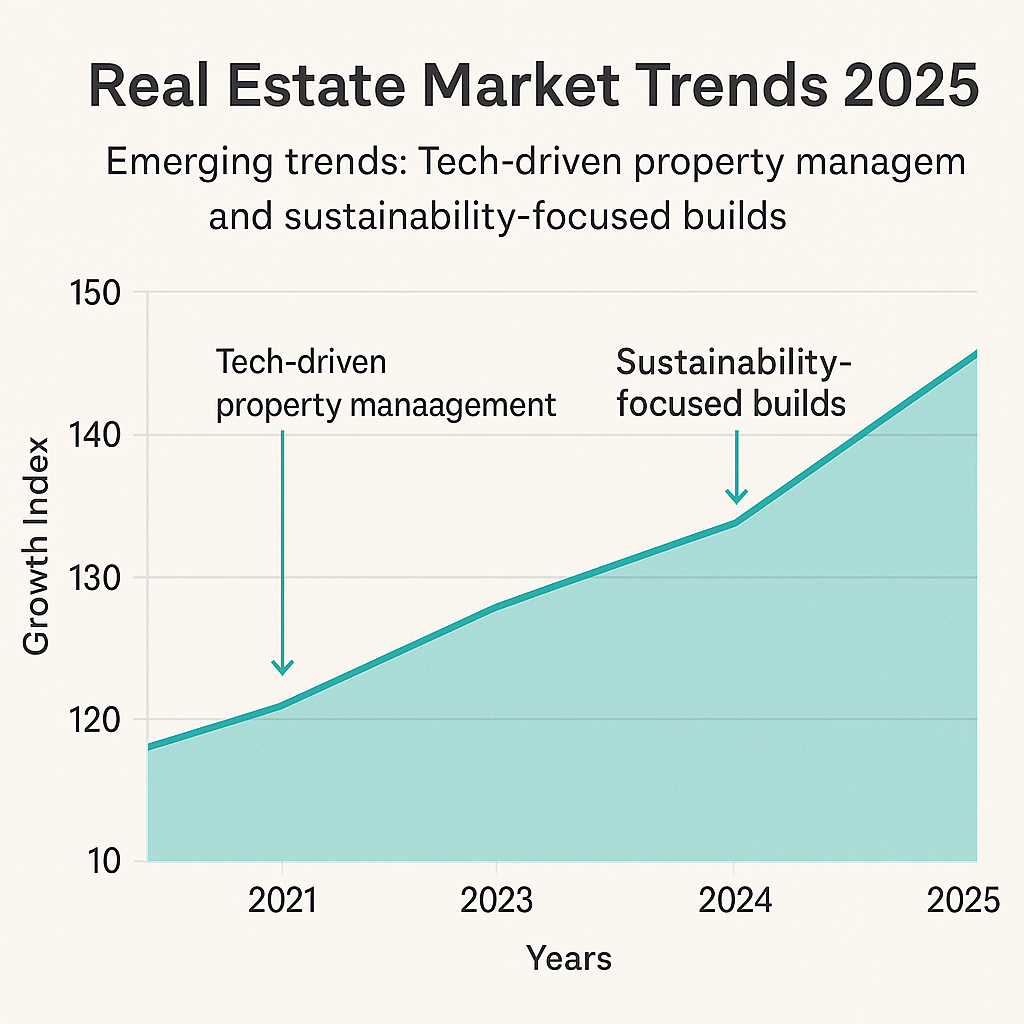
Emerging trends: Tech-driven property management and sustainability-focused builds.
3. How Real Estate Markets Work
Real estate markets operate on supply/demand dynamics, interest rates, and macroeconomic factors. Key drivers include:
- Demographics: Millennials now dominate homebuying (43% of purchases in 2024).
- Interest Rates: Fed rate hikes pushed 30-year mortgage rates to 6.8% in early 2025.
- Zoning Laws: Municipal regulations dictate land use and development potential.
4. Real Estate Investment Strategies
Builds and Buys’ Step-by-Step Invest Guide outlines proven methods:
A. Buy-and-Hold (Rental Properties)
Acquire properties to generate rental income. Example: A $300,000 duplex with 8% annual ROI yields $24,000/year before expenses.
B. Fix-and-Flip
Purchase undervalued homes, renovate, and sell for profit. Pro Tip: Average flip profit was $65,000 in 2024 (ATTOM Data Solutions).
C. REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts)
Invest in publicly traded REITs for liquidity and dividends. Top REITs averaged 10.2% returns over 5 years.
Builds and Buys’ Step-by-Step Framework
Leverage our proprietary systems to minimize risk:
- Research: Use our Buyer’s Toolkit to analyze neighborhoods and comps.
- Finance: Compare loan options (FHA, conventional, hard money).
- Acquire: Negotiate using market-driven data.
- Manage/Exit: Optimize ROI with our Builder’s Checklist.
5. Risks and Challenges
Real estate isn’t without hurdles:
- Market Cycles: Property values fluctuate (e.g., 2008 crash).
- Liquidity: Selling takes time vs. stocks/bonds.
- Maintenance Costs: Budget 1–2% of property value annually for repairs.
6. The Future of Real Estate
Emerging trends to watch:
- Proptech: AI-powered valuations and virtual tours.
- Sustainability: Net-zero buildings and energy-efficient retrofits.
- Co-Living Spaces: Shared housing models for affordability.
Your Tools
Access your tools to manage tasks, update your profile, and track your progress.
Collaboration Feed
Engage with others, share ideas, and find inspiration in the Collaboration Feed.





Leave a Comment